| Furniture Layout Simulation System using a Tablet |
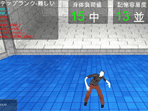
Tablets, which can be operated by touching their screens with fingers in multi-touch systems, are widely being used due to their high portability. In this study, I developed a system for simulating the layout of furniture by freely placing it in 3D space using a tablet. I provide a practical and easy to use system to help people consider the arrangement of their furniture. The system creates a virtual room by arranging furniture from a furniture list after determining the size of the room. Users can place the furniture by a touch operation, which corresponds to such operations as furniture placement. To align the furniture easily, the room is divided into invisible squares along which the furniture is placed. After placing the furniture, users can delete it, change it by a tap, or move it by a drag operation. The system has 25 types of furniture including different size, and a wide variety of indoor spaces can be reproduced. Ten students used the system and evaluated its utility, usability, and problems. The results identified room for improvement in operability and functionality.